Cryptocurrency Taxation Essential
Insights for Digital Asset Investors
As digital currencies become more popular, the issue of cryptocurrency taxation is gaining significance. In many countries, cryptocurrencies are treated as assets, and therefore, they are subject to taxation when bought, sold, or exchanged.
Cryptocurrency and its tax implications, according to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
In the United States, the IRS treats cryptocurrencies as property for tax purposes. Per IRS.gov publication,
digital assets are broadly defined as any digital representation of value which is recorded on a cryptographically secured distributed ledger or any similar technology as specified by the Secretary.
Digital assets include (but are not limited to):
- Convertible virtual currency and cryptocurrency
- Stablecoins
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
Digital assets are not real currency (also known as “fiat”) because they are not the coin and paper money of the United States or a foreign country and are not digitally issued by a government’s central bank.
A digital asset that has an equivalent value in real currency, or acts as a substitute for real currency, has been referred to as convertible virtual currency.
A cryptocurrency is an example of a convertible virtual currency that can be used as payment for goods and services, digitally traded between users, and exchanged for or into real currencies or digital assets
Transactions involving a digital asset are generally required to be reported on a tax return
Taxable income, gain or loss may result from transactions including, but not limited to:
- Sale of a digital asset for fiat
- Exchange of a digital asset for property, goods, or services
- Exchange or trade of one digital asset for another digital asset
- Receipt of a digital asset as payment for goods or services
- Receipt of a new digital asset as a result of a hard fork
- Receipt of a new digital asset as a result of mining or staking activities
- Receipt of a digital asset as a result of an airdrop
- Any other disposition of a financial interest in a digital asset
Note: the transfer of property, including a digital asset, as a bona fide gift, requires the filing of Form 709, United States Gift (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return if the fair market value of the property, at the time of the transfer, exceeds the donor’s annual gift exclusion amount available at the time of the transfer.
Tax Consequences
Any transactions that involve cryptocurrencies are subject to capital gains tax. If you sell, trade, or exchange cryptocurrencies, you may be required to pay taxes on any profits made from these transactions. If an individual buys a cryptocurrency and later sells it at a higher price, they must pay taxes on the profits made from the sale
Crypto tax rates for 2023
When it comes to paying taxes on your cryptocurrency, a few factors come into play. Your taxable income, tax filing status, and the time you held your cryptocurrency before selling it can all impact your tax rate. If you owned your cryptocurrency for 365 days or less before selling it, you must pay short-term gains taxes. On the other hand, if you hold it for a more extended period, you will be subject to long-term gains taxes. It’s essential to keep these factors in mind to ensure that you are properly prepared to pay your taxes and avoid any potential penalties.
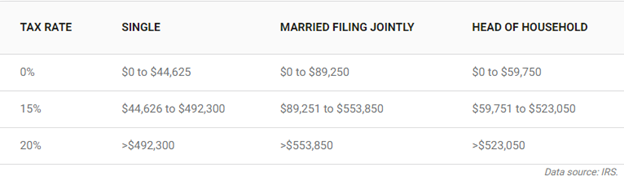
Here are the cryptocurrency tax rates on long-term gains for the 2023 tax year.
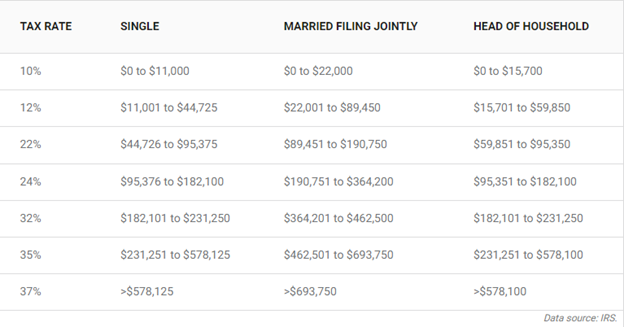
Short-term gains are taxed as ordinary income. Here are the crypto tax brackets on these short-term gains for the 2023 tax year:
In other countries, the taxation of cryptocurrencies may vary, but the general principle of taxing cryptocurrency transactions remains the same. Governments worldwide are increasingly focusing on enforcing tax regulations on cryptocurrencies, and individuals and businesses dealing with digital currencies are advised to stay informed about the tax laws in their respective jurisdictions.
Monitor the regulatory landscape.
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies has been a topic of much debate and discussion in recent years. With the rise in popularity of digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, regulating and overseeing this new form of financial technology has posed a challenge for governments and regulatory bodies worldwide. They have been struggling to find effective ways to address this issue.
In the United States, the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is still evolving, with different agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) all playing a role in overseeing and regulating various aspects of the cryptocurrency market.
Cryptocurrency investors must stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape and seek professional tax advice if necessary. By staying proactive and compliant with tax regulations, investors can avoid potential legal issues and ensure the longevity of their investments in the cryptocurrency market.
Crypto communities engagement
Crypto communities are essential for the growth and development of the digital currency market. These communities, often found on social media platforms and forums, provide a space for individuals to share knowledge, discuss trends, and seek advice from peers. Engaging with these communities is beneficial for staying updated on the latest developments in the industry and crucial for ensuring tax compliance.
With the rise of cryptocurrencies, tax authorities have increasingly focused on ensuring that individuals accurately report their crypto assets and pay the appropriate taxes. However, the constantly evolving nature of the crypto market can make it challenging for taxpayers to understand their reporting obligations. By engaging with crypto communities, individuals can gain insights into best practices for tax compliance and stay informed about new regulatory developments.
Furthermore, active participation in crypto communities allows individuals to seek guidance from experienced members who can provide valuable insights into navigating the complex tax landscape of digital currencies. Individuals need to engage with these communities to ensure they fulfill their tax obligations and stay informed about the ever-changing regulatory environment.
Crypto Tax Software
Crypto tax software has become increasingly popular for individuals and businesses looking to stay tax-compliant in the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency. With the rapid growth of digital currencies over the past decade, the need for accurate and reliable tax reporting has also grown. Crypto tax software solves the complex and often confusing process of reporting cryptocurrency transactions to tax authorities.
For anyone involved in the world of cryptocurrency, using crypto tax software is a must-have tool. It simplifies the process of calculating your taxes and ensures that you’re accurately reporting your earnings and avoiding any potential legal issues. With the constantly changing landscape of cryptocurrency, having reliable and up-to-date tax software can save you time, money, and stress in the long run.
Furthermore, crypto tax software can also help users maximize tax deductions and credits related to their cryptocurrency activities. Users can quickly identify tax-saving opportunities and optimize their tax liabilities by providing comprehensive reports and analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the taxation of cryptocurrencies is an evolving and complex issue that requires a thorough understanding and compliance with tax laws. Both individuals and businesses need to ensure they are meeting their tax responsibilities with respect to cryptocurrency transactions, as the use of digital currencies is becoming increasingly widespread.
References
1. Digital Assets
https://www.irs.gov/businesses/small-businesses-self-employed/digital-assets

Self-employed individuals are often so focused on running their businesses that they may overlook potential tax deductions that could save them money.
Here is the list of the most overlooked deductions for self-employed individuals.
Read more
Tax credits are a powerful tool in the fiscal policy arsenal that governments use to incentivize behavior, support individuals and families, reduce poverty, and stimulate economic activity. Unlike tax deductions, which reduce your taxable income, tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction of tax owed or an increase in a tax refund.
Read more